User Module
By using a user module, you can define and reuse global functions and module functions.
A module is created only once, and the same instance is reused afterwards. During this process, you can perform common initialization tasks, and the values set in the module remain unchanged even if the module is re-imported in the app.

Types of Module Publication
The content written in a module can be exposed via exports and globals.
- exports: Can only be called from the module object. It does not expose to the window object.
- globals: Added to the window, so it can be called from any app. However, conflicts may occur if the window already has properties or classes with the same name.

Exceptions in Module Publication
Since a module is reused, if you set an AppInstance separately for each CLX page, only the last AppInstance will be valid.
In such cases, it is recommended to write and manage a common class inside the module. Add comments to the functions and properties within the class to enable code completion (Content Assist) during development.
Example: util.module.js
/**
* @class Util
* @param {cpr.core.AppInstance} app
*/
var Util = function(app){
this.appInstance = app;
}
/**
* Show a message dialog.
* @param {string} msg
*/
Util.prototype.showMessage = function(msg){
alert(msg);
}
exports.Util = Util;
/**
* Create an instance of the Util class.
* @param {cpr.core.AppInstance}
*/
globals.createUtil = function(app){
return new Util(app);
}Example: hello.clx
var common = cpr.core.Module.require("module/util");
// Using the module
var util = new common.Util(app);
// Using the global function
var util2 = createUtil(app);
// Called when the button is clicked
function buttonClick(event){
util.showMessage("Hello World!");
}Creating a Module
-
You can create a module file by selecting File > New > New Common Module from the global menu or New > New Common Module from the context menu.
-
Global Menu
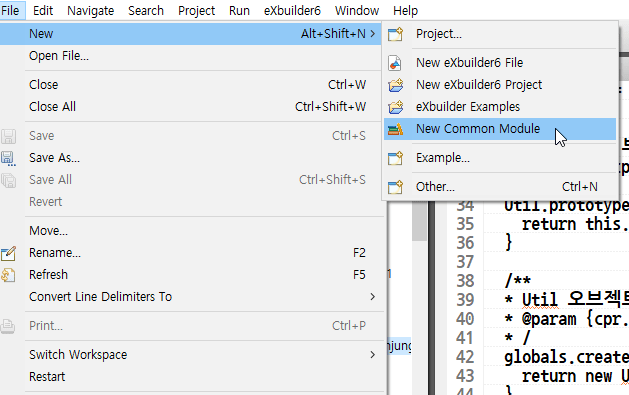
File > New > New Common Module from the Global Menu -
Context Menu
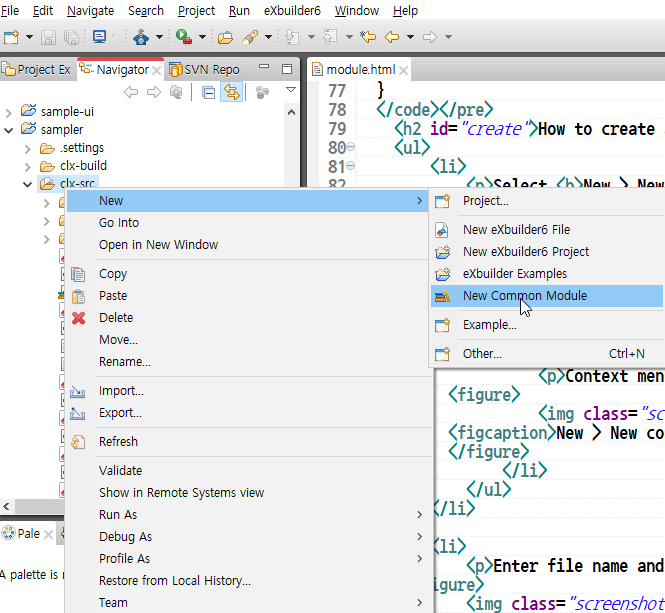
New > New Common Module from the Context Menu
-
-
In the New Common Module wizard, enter the file name and click [Finish] to create the file.
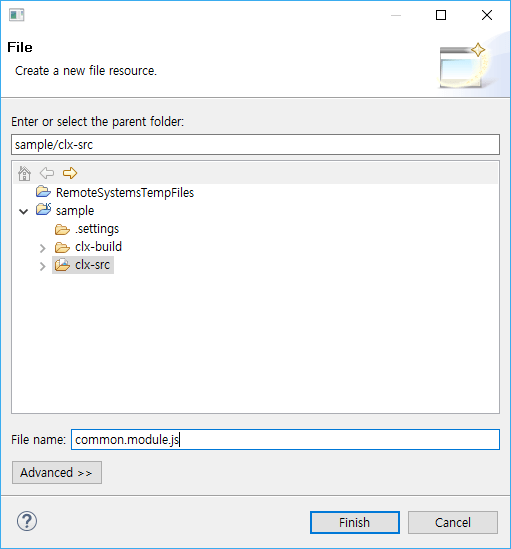
Create a User Module -
Define module functions using
exports.functionNameand global functions usingglobals.functionName.
For example, export themoduleMessagefunction as a module function and theglobalMessagefunction as a global function.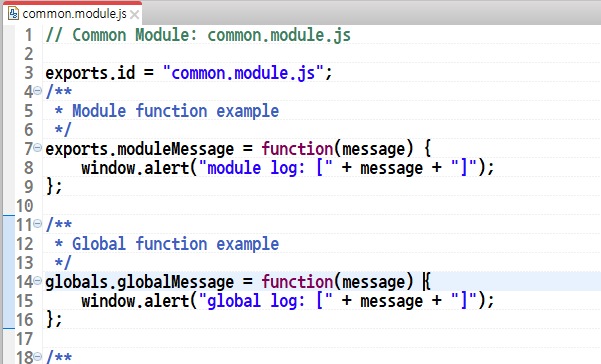
Basic Content of a Module Example: common.module.js
// Common Module: common.module.js exports.id = "common.module.js"; /** * Example of exporting a module function */ exports.moduleMessage = function(message) { window.alert("module log: [" + message + "]"); }; /** * Example of exporting a global function */ globals.globalMessage = function(message) { window.alert("global log: [" + message + "]"); };
Importing a Module
-
In an eXBuilder6 file (*.clx), use
cpr.core.Module.requireto import the written module. Global functions can be used directly without importing the module.// Import a module var commonModule = cpr.core.Module.require("lib.common");
Using a Module
A module is loaded at runtime and its content is executed.
The order of modules written in user-modules.js is not guaranteed, so you cannot import other modules inside a module.
You must use modules only after they have all been loaded.
message.module.js
/**
* Show a message dialog.
* @param {string} msg
*/
exports.showMessage = function(msg){
alert(msg);
}
common.module.js
// (Error) You cannot import another module while a module is being loaded.
// var common= cpr.core.Module.require("module/message");
/**
* @class Util
*/
var Util = function(){
this.msg = cpr.core.Module.require("module/message");
}
/**
* Show a message dialog.
* @param {string} msg
*/
Util.prototype.showMessage= function(msg){
this.msg.showMessage("module log: ["+msg+"]");
}
exports.Util = Util;
globals.showMessage = function(msg){
var message = cpr.core.Module.require("module/message");
message.showMessage("module log: ["+msg+"]");
}
hello.clx
// Import a module
var common = cpr.core.Module.require("module/common");
/*
* Called when the "Module Function" button is clicked.
*/
function onButtonClick(/* cpr.events.CMouseEvent */ e){
common.showMessage("This is a module function.");
}
/*
* Called when the "Global Function" button is clicked.
*/
function onButtonClick2(/* cpr.events.CMouseEvent */ e){
showMessage("This is a global function.");
}
Setting Module Categories
You can assign a category to a user-defined module. Modules are compiled together under the category name. To set a category for a common module after creation, specify it as follows:
module.category("[CategoryName]");
The compiled result of the module will be generated as a file in the following format:
[CategoryName].category.modules.jsExample of compiled modules by category
| Setting | Resulting File Name |
|---|---|
| module.category("unit") | unit.category.modules.js |
| module.category("no") or not specified | no.category.modules.js |
Example: unit.module.js
module.category("unit");
function UnitCategoryKit(appKit) {
this._appKit = appKit;
};
UnitCategoryKit.prototype.getValue = function(app, psCtlId) {
var vcCtl = app.lookup(psCtlId);
return this._appKit.Control.getValue(app, psCtlId);
};
globals.createCategoryKit = function(){
return new UnitCategoryKit(createCommonUtil());
};
Build output in the build directory
unit.category.modules.js
/// start - module/unit/category
(function(){
cpr.core.Module.define("module/unit/category", function(exports, globals, module){
module.category("unit");
function UnitCategoryKit(appKit) {
this._appKit = appKit;
};
UnitCategoryKit.prototype.getValue = function(app, psCtlId) {
var vcCtl = app.lookup(psCtlId);
return this._appKit.Control.getValue(app, psCtlId);
};
globals.createCategoryKit = function(){
return new UnitCategoryKit(createCommonUtil());
};
});
})();
/// end - module/unit/category
Module Without a Category
If you omit the category name in module.category() or specify it as "no", the module will be compiled into no.category.modules.js.
Example: Specified as no
module.category("no");
function NoNCategorizedKit(nck){
this._appKit = nck;
}
NoNCategorizedKit.prototype.getValue = function(app, nckId){
var vCtl = app.lookup(nckId);
return this._appKit.Control.getValue(app.vCtl);
};
globals.createCategoryKit = function(){
return new NoNCategorizedKit(createCommonUtil());
}
Example: Not specified
module.category();
function NoModuleCategoryKit(nmck){
this._appKit = nmck;
}
NoModuleCategoryKit.prototype.getValue = function(app, nmkId){
var vsCtrl = app.lookup(nmkId);
return this._appKit.Control.getValue(app.vsCtrl);
};
globals.createCategoryKit = function(){
return new noModuleCategoryKit(createCommonUtil());
}
Build output in the build directory
no.category.modules.js
/// start - module/internal/no_categorized
(function(){
cpr.core.Module.define("module/internal/no_categorized", function(exports, globals, module){
module.category("no");
function NoNCategorizedKit(nck){
this._appKit = nck;
}
NoNCategorizedKit.prototype.getValue = function(app, nckId){
var vCtl = app.lookup(nckId);
return this._appKit.Control.getValue(app.vCtl);
}
globals.createCategoryKit = function(){
return new NoNCategorizedKit(createCommonUtil());
}
});
})();
/// end - module/internal/no_categorized
/// start - module/no_category
(function(){
cpr.core.Module.define("module/no_category", function(exports, globals, module){
module.category();
function NoModuleCategoryKit(nmck){
this._appKit = nmck;
}
NoModuleCategoryKit.prototype.getValue = function(app, nmkId){
var vsCtrl = app.lookup(nmkId);
return this._appKit.Control.getValue(app.vsCtrl);
}
globals.createCategoryKit = function(){
return new noModuleCategoryKit(createCommonUtil());
}
});
})();
/// end - module/no_category
Module Content Assist
If a module is written correctly, you can use Content Assist (
-
Global functions provide Content Assist directly in an eXBuilder6 file (*.clx).
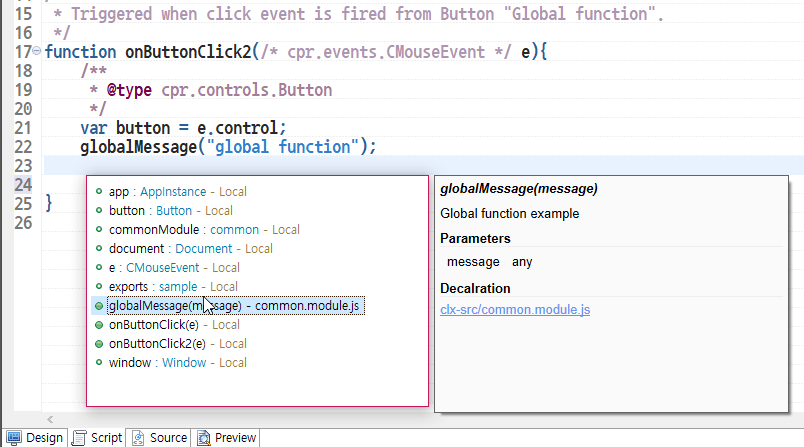
Content Assist for a Module's Global Function -
Module functions provide Content Assist when you use the imported module.
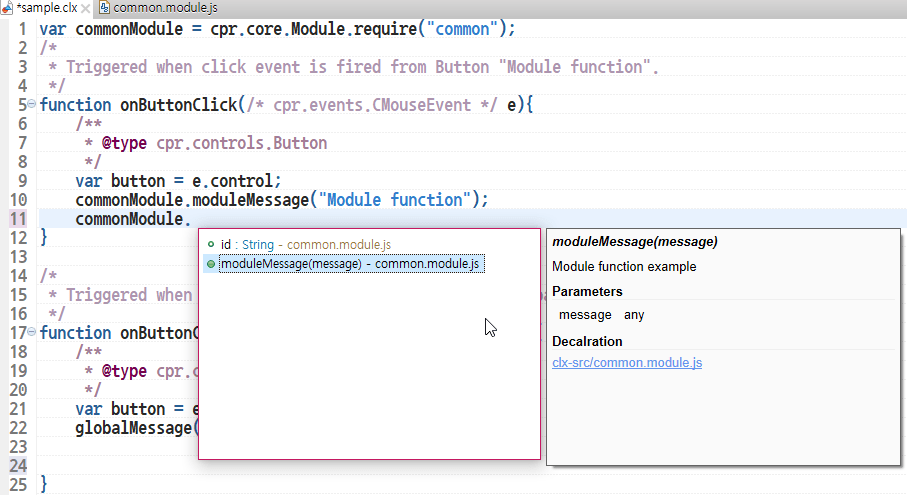
Content Assist for Exported Properties and Functions
How to Write Comments for Content Assist
- @param: Describes a parameter. Written as type, name, and description.
Example) @param {String} id ID of the object to find.
- @return: Describes the function’s return value. Written as type and description.
Example) @return {cpr.core.Identifiable} The object with the specified ID
/**
* Common Utility Class
*/
{
var ComUtil = function(/* cpr.core.AppInstance */app) {}
/**
* Add your description here.
*
* @param {String} id ID of the object to find.
* @return {cpr.core.Identifiable} The object with the specified ID
*/
ComUtil.prototype.getObject = function(/*string*/id){}
globals.createComUtil = function(/* cpr.core.AppInstance */app) {
return new ComUtil(app);
}
}
User Content Assist
-
@param: Describes a parameter.
If it is a control type + Id, the Id values of the control type are shown in Content Assist.
If the last value is Id, the type is String. If it’s idx, the type is Number. Otherwise, it’s any.
Example) @param {String} buttonId.
/**
* Add your description here.
*
* @param {String} buttonId
*
*/
function test(buttonId){
test(Ctrl + Space )
}